In this post, we will see how we can implement the MVC (Model-View-Controller) design pattern in ABAP using the Objects. If you have not read the previous discussion about MVC: ABAP Objects Design Patterns – Model View Controller (MVC) Part 1, than I strongly recommond to read that before moving forward.
Demo Application
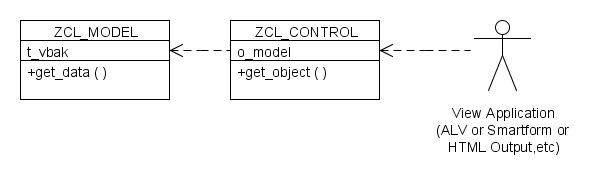
To implement the MVC, we will create two applications – One will generate an output in ALV and other will generate an output Smartforms. We will put our business logic in the MODEL class. We will create one CONTROL class to establish control between Model and Views.
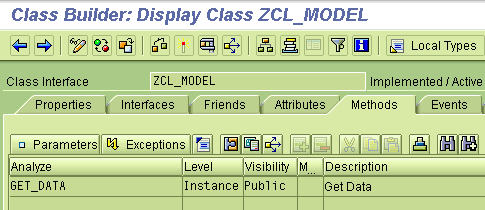
Our business logic for this example is fairly simple – select the Sales Orders from the VBAK which were created in last ten days. The public method GET_DATA in the class ZCL_MODEL will act as the business logic. Additionally, this class has the public attribute T_VBAK which will be set by the GET_DATA and hold our data from the table.
UML
The UML diagram for any of the application would be like:
Model Class Setup
Model Method Definition
Model Attribute definition
Code Snippet of method GET_DATA
This code would be implemented in the method GET_DATA
* Parameters * Importing IR_ERDAT TYPE TPMY_R_DATE Ranges for date * METHOD get_data. * * Get data and save into attribute T_VBAK SELECT * FROM vbak INTO TABLE t_vbak WHERE erdat IN ir_erdat. * * ENDMETHOD.
Controller Class Setup
Our controller class ZCL_CONTROL will have a method GET_OBJECT which will give us an object of the model class. We require a public attribute which can refer to the object created in the method GET_OBJECT.
Controller Method definition:
Controller Attributes definition:
Code Snippet for method GET_OBJECT:
* Parameters * Importing IF_NAME TYPE CHAR30 Model class name * METHOD get_object . * DATA: lo_object TYPE REF TO object. * * Generic object reference to importing class CREATE OBJECT lo_object TYPE (if_name). IF sy-subrc = 0. * Downcasting to assign generic object to O_MODEL o_model ?= lo_object. ENDIF. * ENDMETHOD.
In the next post we will see, how we will use the controller class in our view and access the business logic encapsulated in Model class.
Related Links:
- ABAP Objects Design Patterns – Model View Controller (MVC) Part 1
- ABAP Objects Design Patterns – Model View Controller (MVC) Part 3
SDN Wiki – Model View Controller design Pattern



Hello Naimesh,
Thanks for the great article.
Controller Attributes definition is the class ZCL_CONTROL. It is changed the picture, showing from another class ZCL_MODEL.
May I know how you define the o_model?
Thanks,
Miguel
Hello Miguel,
Thanks for pointing out the missing piece. I have corrected it not.
Basically, O_MODEL is reference to the ZCL_MODEL.
Regards,
Naimesh Patel
great help
Hello,
great example! How do I get the neccessary information (if_name) to instantiate the o_model object?
thanx in advance
Patrick
I’m sorry, of course i meant the lo_object in the get_object method.
Hello Patrick,
IF_NAME is part of the signature of the method GET_OBJECT. The application will pass the name of the required object.
Please refer to Model View Controller (MVC) Part 3 for code on which we pass ZCL_MODEL in IF_NAME to instantiate the object.
* Get the object from Control
CALL METHOD lo_control->get_object
EXPORTING
if_name = 'ZCL_MODEL'.
Of course, we need to implement exception handling in the method GET_OBJECT, which can be raised if we don’t find any corresponding class name.
Regards,
Naimesh Patel